 Location: Ch 7: Properties of Matter
Location: Ch 7: Properties of Matter

 Location: Ch 7: Properties of Matter
Location: Ch 7: Properties of Matter
|
 |
PROPERTIES OF MATTER
IN THIS CHAPTER:
|
 nergy can manifest itself as matter. All matter in the universe was created
with and cannot exist without energy. When matter is broken down, the powder
that results is made of many billions of tiny particles known as atoms.
There are about 110 elements in the periodic table, of which 90 occur naturally.
An element is a specific configuration of an atom that lists properties
such as number of protons, electrons (in an uncharged atom) and neutrons,
atomic number, the atomís symbol and name, its atomic mass, the number
of isotopes it can have, melting and boiling points, number of valence
atoms and length of the atomís half-life (for radioactive elements). Almost
every single substance in the universe is made up of less than 100 elements.
nergy can manifest itself as matter. All matter in the universe was created
with and cannot exist without energy. When matter is broken down, the powder
that results is made of many billions of tiny particles known as atoms.
There are about 110 elements in the periodic table, of which 90 occur naturally.
An element is a specific configuration of an atom that lists properties
such as number of protons, electrons (in an uncharged atom) and neutrons,
atomic number, the atomís symbol and name, its atomic mass, the number
of isotopes it can have, melting and boiling points, number of valence
atoms and length of the atomís half-life (for radioactive elements). Almost
every single substance in the universe is made up of less than 100 elements.
| The 16 Most Common Elements on Earth | |
| Aluminum (Al) | Nitrogen (N) |
| Calcium (Ca) | Oxygen (O) |
| Carbon (C ) | Phosphorus (P) |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Potassium (K) |
| Fluorine (F) | Silicon (Si) |
| Hydrogen (H) | Sodium (Na) |
| Iron (Fe) | Sulfur (S) |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Titanium (Ti) |
Atoms are infinitesimally small. In a gram of water there are at least 1023 atoms, which is more than the number of the drops in all the lakes, rivers and oceans in the world. In an average personís lungs there are as many atoms in the air as there are breaths in the atmosphere. Atoms are always moving, continuously powered by energy. In solids, the amount of movement is very little, while atoms move very quickly in a gas. It only takes about six years for somebodyís breath to become evenly mixed in the entire atmosphere. At that point, every person on Earth has inhaled at least one of the atoms that you have exhaled. Atoms cannot be seen in a light microscope because atoms are smaller than the wavelengths of light. In order to see an atom, one must use an electron microscope or a scanning tunnel microscope. Brownian motion is the constant jiggling of atoms resulting from the motion of neighboring atoms and molecules.
Atoms can combine to form larger particles known as molecules. For example, two hydrogen (H2) atoms can bond with oxygen (O) to form a water molecule (H2O). Matter that is a gas or a liquid at room temperature is usually made of compound molecules. However, not all matter is made of molecules. Metals and crystalline materials are made of atoms that are not joined as molecules. Atoms can also form in compounds. A compound is a substance that consists of different elements in fixed proportions. The chemical formula of the compound tells the proportions of each element. A compound may or may not be made of molecules. Some compounds are made of atoms arranged in pattern.
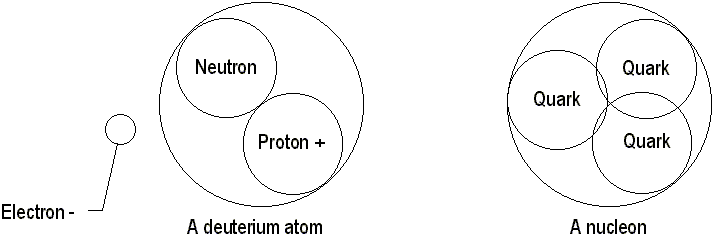
Atoms are mostly empty space. However, nearly all the mass is packed into a ball known as the nucleus. Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus after he shot alpha particles at some gold foil. He reasoned that this nucleus occupied the center of the atom while most of the atom itself was empty space. He was correct. There is so much empty space inside an atom that if the nucleus was the size of a tennis ball, the atom itself would be as big as a stadium! Nuclei are made of nucleons, which have a mass of 1 amu (Atomic Mass Unit). Nucleons without charge are known as neutrons, and charged nucleons are protons. All nucleons are identical copies of each other. Nucleons are not actual particles; they are made of even tinier quarks, which are held together by gluons. Any atoms with the same number of protons are all of the same element. The number of protons determines the elementís atomic number. However, the same does not work for neutrons. Atoms that have different numbers of neutrons are known a
 There are two
types of charges: positive and negative. Inside an atom, protons are positively
charged, neutrons have no charge and electrons have a negative charge.
When the number of electrons equals the number of protons the atomís net
charge is neutral. Any atom with a charge of any kind is called an ion.
Since positive and negative charges attract each other, electrons are held
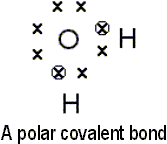
in orbit of the nucleus by centripetal force. Covalent bonds are created
when two atoms share each otherís electrons to become more perfect (that
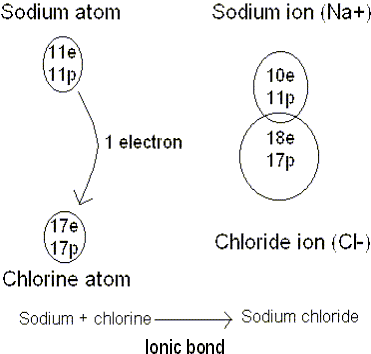
is, with zero or eight electrons). Ionic bonds form when atoms transfer
electrons between themselves. Although there is a lot of empty space in
an atom, people do not fall through the floor because the forces of repulsion
prevent atoms from caving in on each other under pressure. Another type
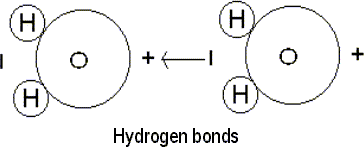
of bond, the hydrogen bond, is formed when two charged atoms attract each
other.
There are two
types of charges: positive and negative. Inside an atom, protons are positively
charged, neutrons have no charge and electrons have a negative charge.
When the number of electrons equals the number of protons the atomís net
charge is neutral. Any atom with a charge of any kind is called an ion.
Since positive and negative charges attract each other, electrons are held
in orbit of the nucleus by centripetal force. Covalent bonds are created
when two atoms share each otherís electrons to become more perfect (that
is, with zero or eight electrons). Ionic bonds form when atoms transfer
electrons between themselves. Although there is a lot of empty space in
an atom, people do not fall through the floor because the forces of repulsion
prevent atoms from caving in on each other under pressure. Another type
of bond, the hydrogen bond, is formed when two charged atoms attract each
other.
The periodic table is a chart that lists atoms by their atomic number
and electron configuration. As you go across, the elements increase in
number. As you move down, each element has one more electron energy level
 filled with electrons. Elements in the same column have similar properties
and react in similar ways.
filled with electrons. Elements in the same column have similar properties
and react in similar ways.
Matter exists in four phases. The three most common are solids, liquids
and gases. The fourth phase is known as the plasma phase. Plasma consists
of positively charged ions and free electrons. Plasmas exist only at very
high temperatures (above 2000°C). Plasma is the predominant form of
matter in the universe. Stars and much of the intergalactic matter are
 in the plasma phase. Fluorescent lights use plasmas as well. In all phases
of matter, atoms are always in constant motion. Atoms in solid matter vibrate
in a fixed position. If heat energy is applied to the material, the atoms
will break loose and wander through the material. Now the substance forms
the shape of its container; it is a liquid. If even more heat energy is
applied to the liquid, the atoms will break away from each other and the
material will form a gas. If an even greater amount of heat is applied
(2000°C), electrons will have enough energy to break away from the
atom. Thus plasma is formed.
in the plasma phase. Fluorescent lights use plasmas as well. In all phases
of matter, atoms are always in constant motion. Atoms in solid matter vibrate
in a fixed position. If heat energy is applied to the material, the atoms
will break loose and wander through the material. Now the substance forms
the shape of its container; it is a liquid. If even more heat energy is
applied to the liquid, the atoms will break away from each other and the
material will form a gas. If an even greater amount of heat is applied
(2000°C), electrons will have enough energy to break away from the
atom. Thus plasma is formed.
In conclusion, all matter is made from and sustained by energy. All matter consists of tiny building blocks known as atoms. Of these atoms, there are only about 110 distinct types of atoms. Most of these atoms have been recycled through matter for billions of years. They are much too small to be seen with visible light but they can be photographed with an electron or scanning-tunnel microscope. A compound is a substance made of different elements combined in a fixed proportion. Some compounds are made of molecules in any particular arrangement while others have atoms arranged in a regular pattern. Atoms are mostly empty space. The mass of an atom is almost entirely in the nucleus, which is made up of neutrons and protons. The number of protons determines the atomís atomic number. There are two charges, positive and negative. A neutral atom has the same number of protons as electrons. Lastly, the periodic table is a chart of elements arranged according to similar structure and similar properties

 Location: Ch 7: Properties of Matter
Location: Ch 7: Properties of Matter
|